Table of Contents
3. Spark Core 基本用法
Programming in Spark
1. 创建RDD,Create RDDs
2. 应用转换, Apply transformations
3. 执行,Perform actions
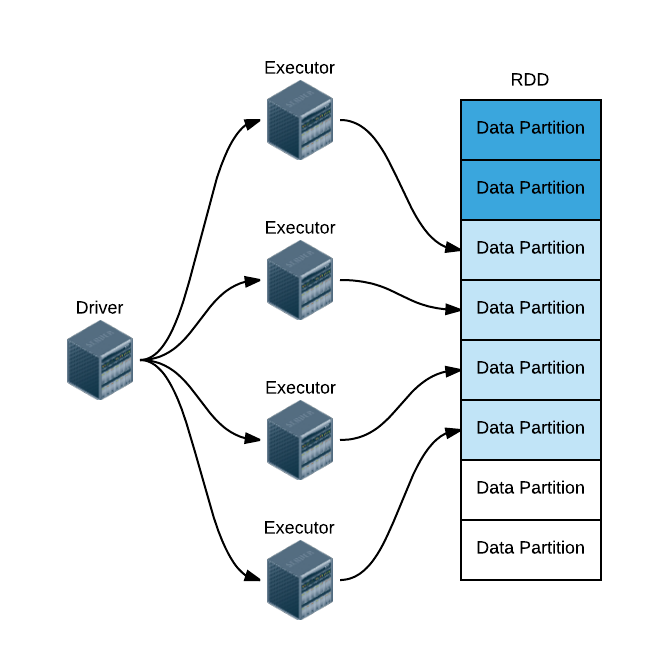
RDD,全称为 Resilient Distributed Datasets,是一个容错的、并行的数据结构,可以让用户显式地将数据存储到磁盘和内存中,并能控制数据的分区。
RDD 是不可变Java虚拟机(JVM)对象的分布式集合。我们使用python时候,尤其要注意,python数据是存储在JVM对象中的
3.1. Create RDDs
# 1.SparkContext 类 class pyspark.SparkContext ( master = None, appName = None, sparkHome = None, pyFiles = None, environment = None, batchSize = 0, serializer = PickleSerializer(), conf = None, gateway = None, jsc = None, profiler_cls = <class 'pyspark.profiler.BasicProfiler'> ) # 以下是SparkContext的参数。 # Master - 它是连接到的集群的URL。 # appName - 您的工作名称。 # sparkHome - Spark安装目录。 # pyFiles - 要发送到集群并添加到PYTHONPATH的.zip或.py文件。 # environment - 工作节点环境变量。 # batchSize - 表示为单个Java对象的Python对象的数量。 设置1以禁用批处理,设置0以根据对象大小自动选择批处理大小,或设置为-1以使用无限批处理大小。 # serializer - RDD序列化器。 # Conf - L {SparkConf}的一个对象,用于设置所有Spark属性。 # gateway - 使用现有网关和JVM,否则初始化新JVM。 # JSC - JavaSparkContext实例。 # profiler_cls - 用于进行性能分析的一类自定义Profiler(默认为pyspark.profiler.BasicProfiler)。 # 2.SparkContext 类 class pyspark.RDD ( jrdd, ctx, jrdd_deserializer = AutoBatchedSerializer(PickleSerializer()) )
from pyspark import SparkContext sc = SparkContext("local", "count app") # 1 从内存中读取并行集合 data = sc.parallelize( [('Amber', 22), ('Alfred', 23), ('Skye',4), ('Albert', 12), ('Amber', 9)]) # 2 从硬盘中读取 # 本地文件系统,HDFS,Cassandra,HBase,Amazon S3等。 Spark 支持文本文件(text files),SequenceFiles 和其他 Hadoop InputFormat。 data_from_file = sc.textFile('/Users/drabast/Documents/PySpark_Data/VS14MORT.txt.gz',4) ## 4: Parallelize range output into 4 partitions
3.2. Apply transformations
| ransformation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| map(func) | 返回一个新的分布式数据集,将数据源的每一个元素传递给函数 func 映射组成。 |
| filter(func) | 返回一个新的数据集,从数据源中选中一些元素通过函数 func 返回 true。 |
| flatMap(func) | 类似于 map,但是每个输入项能被映射成多个输出项(所以 func 必须返回一个 Seq,而不是单个 item)。 |
| mapPartitions(func) | 类似于 map,但是分别运行在 RDD 的每个分区上,所以 func 的类型必须是 Iterator |
| mapPartitionsWithIndex(func) | 类似于 mapPartitions,但是 func 需要提供一个 integer 值描述索引(index),所以 func 的类型必须是 (Int, Iterator) => Iterator 当运行在类型为 T 的 RDD 上。 |
| sample(withReplacement, fraction, seed) | 对数据进行采样。 |
| union(otherDataset) | Return a new dataset that contains the union of the elements in the source dataset and the argument. |
| intersection(otherDataset) | Return a new RDD that contains the intersection of elements in the source dataset and the argument. |
| distinct([numTasks])) | Return a new dataset that contains the distinct elements of the source dataset. |
| groupByKey([numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, Iterable) pairs. Note: If you are grouping in order to perform an aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using reduceByKey or combineByKey will yield much better performance. Note: By default, the level of parallelism in the output depends on the number of partitions of the parent RDD. You can pass an optional numTasks argument to set a different number of tasks. |
| reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function func, which must be of type (V,V) => V. Like in groupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument. |
| aggregateByKey(zeroValue)(seqOp, combOp, [numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, U) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given combine functions and a neutral "zero" value. Allows an aggregated value type that is different than the input value type, while avoiding unnecessary allocations. Like in groupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument. |
| sortByKey([ascending], [numTasks]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs where K implements Ordered, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs sorted by keys in ascending or descending order, as specified in the boolean ascending argument. |
| join(otherDataset, [numTasks]) | When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key. Outer joins are also supported through leftOuterJoin and rightOuterJoin. |
| cogroup(otherDataset, [numTasks]) | When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, Iterable, Iterable) tuples. This operation is also called groupWith. |
| cartesian(otherDataset) | When called on datasets of types T and U, returns a dataset of (T, U) pairs (all pairs of elements). |
| pipe(command, [envVars]) | Pipe each partition of the RDD through a shell command, e.g. a Perl or bash script. RDD elements are written to the process's stdin and lines output to its stdout are returned as an RDD of strings. |
| coalesce(numPartitions) | Decrease the number of partitions in the RDD to numPartitions. Useful for running operations more efficiently after filtering down a large dataset. |
| repartition(numPartitions) | Reshuffle the data in the RDD randomly to create either more or fewer partitions and balance it across them. This always shuffles all data over the network. |
3.3. Perform actions
| Action | Meaning |
|---|---|
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). The function should be commutative and associative so that it can be computed correctly in parallel. |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. This is usually useful after a filter or other operation that returns a sufficiently small subset of the data. |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset (similar to take(1)). |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. Note that this is currently not executed in parallel. Instead, the driver program computes all the elements. |
| takeSample(withReplacement, num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, optionally pre-specifying a random number generator seed. |
| takeOrdered(n, [ordering]) | Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator. |
| saveAsTextFile(path) | Write the elements of the dataset as a text file (or set of text files) in a given directory in the local filesystem, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. Spark will call toString on each element to convert it to a line of text in the file. |
| saveAsSequenceFile(path) (Java and Scala) | Write the elements of the dataset as a Hadoop SequenceFile in a given path in the local filesystem, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. This is available on RDDs of key-value pairs that either implement Hadoop's Writable interface. In Scala, it is also available on types that are implicitly convertible to Writable (Spark includes conversions for basic types like Int, Double, String, etc). |
| saveAsObjectFile(path) (Java and Scala) | Write the elements of the dataset in a simple format using Java serialization, which can then be loaded using SparkContext.objectFile(). |
| countByKey() | Only available on RDDs of type (K, V). Returns a hashmap of (K, Int) pairs with the count of each key. |
| foreach(func) | Run a function func on each element of the dataset. This is usually done for side effects such as updating an accumulator variable (see below) or interacting with external storage systems. |
Some Common Actions
Action Usage collect() Copy all elements to the driver take(n) Copy first n elements reduce(func) Aggregate elements with func (takes 2 elements, returns 1) saveAsTextFile(filename) Save to local file or HDFS
Spark的三种模式的详细运行过程(基于standalone与基于yarn)
Spark部署在单台机器上面时,可以使用本地模式(Local)运行;当部署在分布式集群上面的时候,可以根据自己的情况选择Standalone模式(Spark自带的模式)、YARN-Client模式或者YARN-Cluster模式、Spark on Mesos模式。
https://blog.csdn.net/wyqwilliam/article/details/84678867
